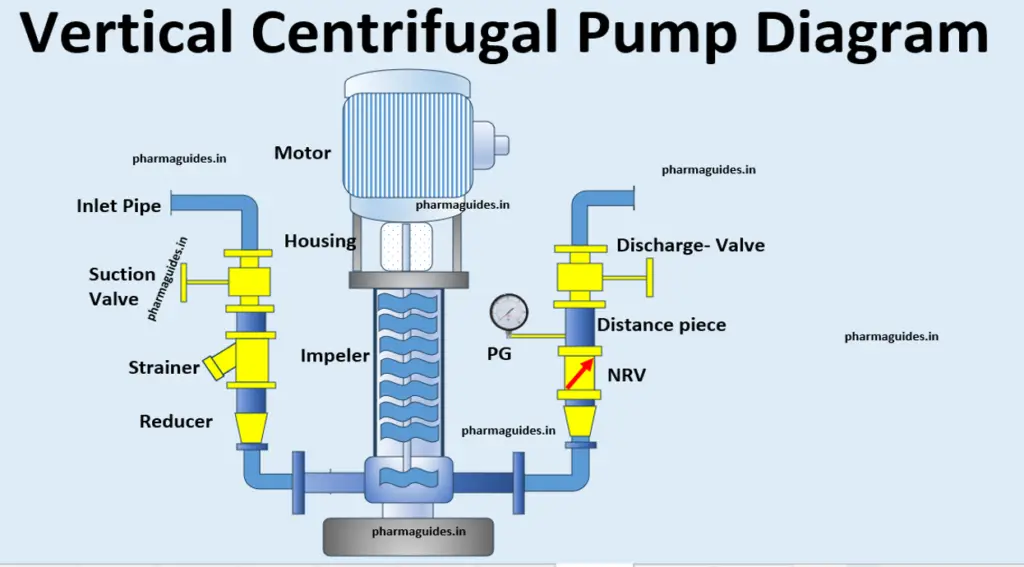
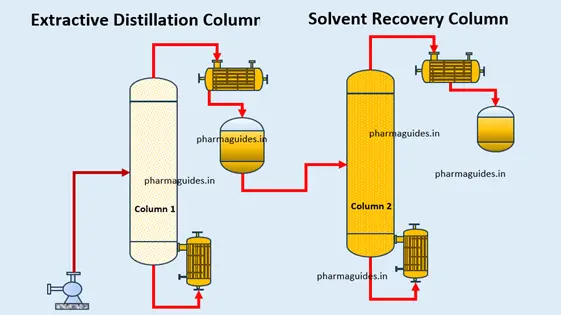
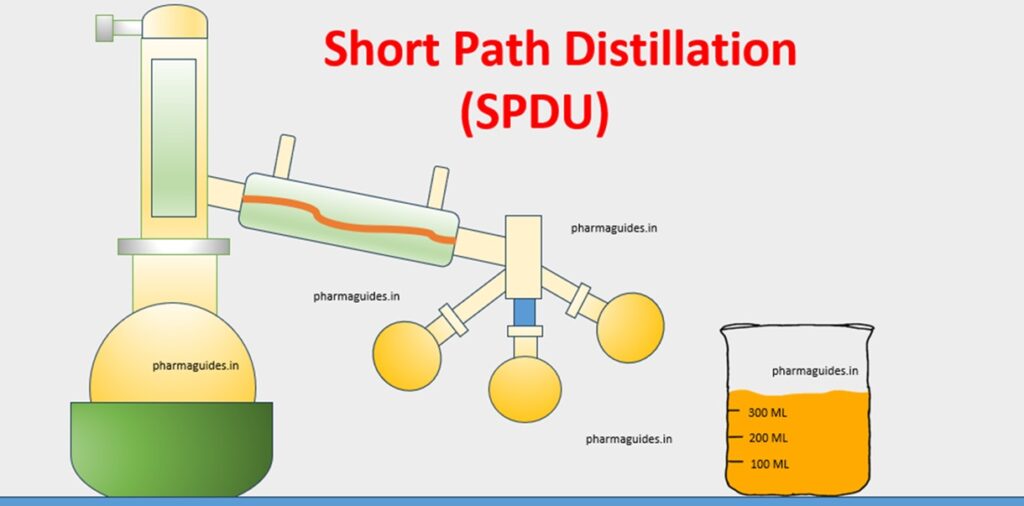
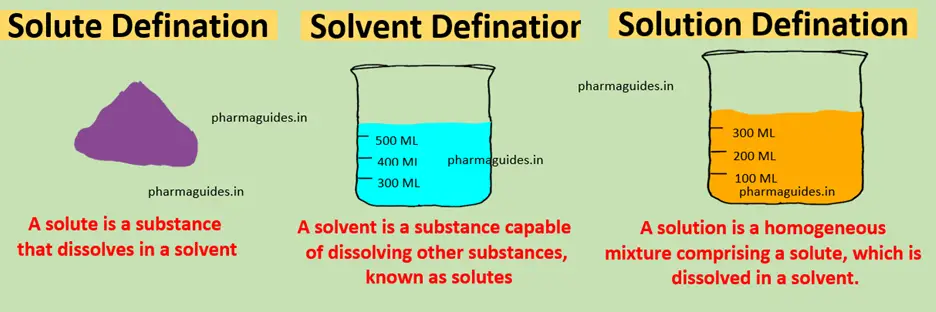
Article Contents
ch triple bond ch
Unraveling the Marvels of the Carbon-Hydrogen Triple Bond
Introduction: Chemistry is a realm of wonder, where the tiniest interactions between atoms can have profound effects on the properties and behaviors of substances. Within this vast domain, the carbon-hydrogen triple bond, or the CH triple bond, stands as a remarkable phenomenon. While carbon-carbon and carbon-oxygen bonds often steal the spotlight, the CH triple bond possesses its own distinctive charm, providing a platform for exploration and innovation in various scientific fields. In this article, we delve into the unique characteristics and applications of this intriguing bond (triple bond examples).

Understanding the CH Triple Bond
The carbon-hydrogen triple bond consists of three shared electron pairs between a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom. It is a relatively rare occurrence in nature, as carbon typically prefers to form four bonds in its stable state. Nevertheless, under certain conditions, the CH triple bond can be created and studied, revealing fascinating insights into the world of chemical bonding.

triple bond examples
Unique Bond Strength: The CH triple bond is known for its exceptional strength, displaying robustness in the face of chemical reactions. This strength arises from the overlap of the atomic orbitals of carbon and hydrogen atoms, resulting in a higher bond dissociation energy compared to other carbon-hydrogen bonds. This inherent stability makes the CH triple bond crucial in the design of high-energy materials, such as rocket propellants and explosives (triple bond examples).
Applications in Organic Synthesis
Organic chemistry relies heavily on the CH triple bond for synthetic purposes. The ability to selectively break and form carbon-hydrogen bonds opens up a vast array of possibilities for creating complex molecules. Transition metal catalysts, such as palladium, platinum, and rhodium, facilitate the activation of the CH triple bond, enabling chemists to carry out efficient transformations. These reactions have revolutionized the field, allowing for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other valuable compounds (triple bond examples).
Exploring the Realm of Carbyne
At the heart of the CH triple bond lies the elusive carbyne, a one-dimensional carbon chain with alternating single and triple bonds. Carbyne possesses extraordinary properties, including exceptional mechanical strength and electrical conductivity. Scientists have been fascinated by its potential applications in nanotechnology, energy storage, and as a building block for advanced materials. Although synthesizing and manipulating carbyne remains a considerable challenge, researchers continue to explore its intriguing properties and potential applications.
Environmental Implications: The study of the CH triple bond extends beyond the laboratory, offering insights into environmental processes. Understanding the kinetics and reactivity of carbon-hydrogen bonds is crucial in atmospheric chemistry, as these bonds play a significant role in the breakdown of organic compounds in the atmosphere. By comprehending the behavior of the CH triple bond, scientists can develop strategies to mitigate air pollution, enhance air quality, and better comprehend the complex interactions occurring in our atmosphere(ch triple bond ch).
FNQs
Q: What is the IUPAC name of CH ≡ C CH3?
The IUPAC name of CH ≡ C CH3 is propyne.
Q: What is ch3c ≡ CH?
The compound ch3c ≡ CH is known as ethynylmethylenecarben.
Q: What is the formula for CH triple bond CH?
The formula for CH triple bond CH is C2H2.
Q: What is the IUPAC name of CH ≡ C CH CH2?
The IUPAC name of CH ≡ C CH CH2 is 2-butyne.
Q: Which elements form triple bonds?
Triple bonds are most commonly formed between carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) atoms. However, other elements such as oxygen (O), sulfur (S), and phosphorus (P) can also form triple bonds in certain compounds(ch triple bond ch).
Q: What is a double and triple bond with examples?
A double bond is a chemical bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. It is represented by a double line (═) in structural formulas. An example of a compound with a double bond is ethene (C2H4), where there is a double bond between the two carbon atoms.
A triple bond, on the other hand, is a chemical bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. It is represented by a triple line (≡) in structural formulas. An example of a compound with a triple bond is ethyne (C2H2), also known as acetylene, where there is a triple bond between the two carbon atoms.
Q: What is a triple bond?
A triple bond is a type of covalent bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms. It is the strongest and shortest type of covalent bond, characterized by a high bond energy and a shorter bond length compared to single or double bonds. Triple bonds exhibit a higher degree of rigidity and provide additional stability to molecules.
Q: Is O2 a triple bond?
No, O2 does not have a triple bond. Oxygen molecules (O2) consist of a double bond between the two oxygen atoms, where two pairs of electrons are shared (ch triple bond ch).
Q: Is N2 a triple bond?
Yes, N2 has a triple bond. Nitrogen molecules (N2) are composed of two nitrogen atoms bonded together by a triple bond, where three pairs of electrons are shared. This triple bond in N2 gives nitrogen gas its remarkable stability and inertness under normal conditions.
Conclusion
The carbon-hydrogen triple bond, with its unique characteristics and versatile applications, continues to captivate scientists across various disciplines. From its strength and stability in high-energy materials to its role in organic synthesis and environmental processes, this bond represents a gateway to exploring new frontiers in chemistry. As research advances, unveiling the mysteries of the CH triple bond will undoubtedly lead to breakthroughs that shape the future of science, technology, and our understanding of the world around us.
Read Also,