5.6 difference between extractive and azeotropic distillation
Article Contents
difference between extractive and azeotropic distillation
difference between extractive and azeotropic distillation :- Distillation- is a process of separating components of a mixture by using the difference in boiling points. It is widely used in various industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing. There are different types of distillation techniques, including extractive type distillation and azeotropic distillation. Although both techniques are used for separating components, they have some differences that make them unique. In this article, we will explore the difference between extractive and azeotropic distillation.

Extractive Distillation
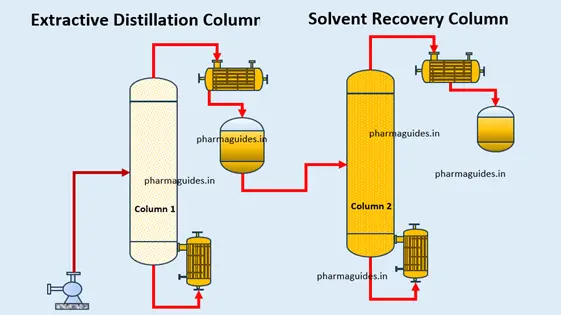
Extractive distillation is a process in which a third component is added to the mixture to facilitate the separation of the components. The added component, known as the solvent, forms a separate liquid phase with one of the components and alters the relative volatility of the components. This results in the formation of an azeotrope, which is a mixture that boils at a constant temperature and has a composition different from the original mixture.
The solvent used in extractive type distillation should have a higher boiling point than the mixture’s components and should be immiscible with the other components. The solvent’s choice depends on the specific application, but common solvents used include glycols, amides, and ketones.
Extractive distillation is useful in separating azeotropic mixtures or mixtures that have a small difference in boiling points. It is commonly used in the production of high-purity chemicals, such as ethanol, where it is challenging to achieve a high degree of separation using conventional distillation techniques.

Azeotropic Distillation
Azeotropic distillation is a process in which a mixture of two or more components is boiled and the vapor is condensed to form a liquid with a fixed composition. The liquid obtained is known as an azeotrope, which has a boiling point lower or higher than the original mixture, depending on the components’ relative volatilities.
Azeotropic distillation is used to separate components with similar boiling points that cannot be separated by conventional distillation techniques. The azeotropic mixture’s composition is such that it has a lower or higher boiling point than the individual components, making separation possible.
The azeotropic mixture’s composition depends on the mixture’s components, and it can be altered by adding a third component, known as an entrainer. The entrainer should be miscible with the azeotrope and have a different boiling point than the mixture’s components. The entrainer forms a separate liquid phase with the azeotrope, altering its composition and allowing the separation of the components.
Difference between Extractive and Azeotropic Distillation
The main difference between extractive and azeotropic distillation is the addition of a third component in extractive distillation. In azeotropic distillation, the components are boiled to form an azeotrope, while in extractive distillation, a solvent is added to facilitate separation.
Another difference is that in extractive distillation, the solvent forms a separate liquid phase with one of the components, while in azeotropic distillation, the entrainer forms a separate liquid phase with the azeotrope.
Additionally, extractive distillation is used to separate azeotropic mixtures or mixtures with a small difference in boiling points, while azeotropic distillation is used to separate components with similar boiling points that cannot be separated by conventional distillation techniques.
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between extractive and azeotropic distillation:
| Parameter | Extractive Distillation | Azeotropic Distillation |
|---|---|---|
| Third Component | Solvent added to mixture | Entrainer added to azeotrope |
| Purpose | Facilitate separation | Alter azeotrope composition |
| Liquid Phases | Solvent forms separate phase | Entrainer forms separate phase |
| Boiling Point Difference | Small | Similar |
| Application | Azeotropic mixtures | Components with similar BP |
I hope you find this helpful!
QNA on difference between extractive and azeotropic distillation
What is the main advantage of using extractive distillation?
Extractive distillation can separate azeotropic mixtures or mixtures with a small difference in boiling points, which is difficult to achieve with conventional distillation techniques.
How does the choice of solvent affect the efficiency of extractive distillation?
The choice of solvent is crucial in extractive distillation as it affects the degree of separation and energy consumption. The solvent should have a high boiling point, be immiscible with the other components, and form a separate phase with one of the components.
What is an azeotrope?
An azeotrope is a mixture of two or more components that has a constant boiling point and a composition different from the original mixture. Azeotropes are difficult to separate by conventional distillation techniques.
What is an entrainer in azeotropic distillation?
An entrainer is a third component added to an azeotropic mixture to alter its composition and facilitate separation. The entrainer should be miscible with the azeotrope and have a different boiling point than the mixture’s components.
What industries use extractive and azeotropic distillation?
Extractive and azeotropic distillation are widely used in various industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing. These techniques are useful in separating high-purity chemicals, such as ethanol, and in producing specialty chemicals.
How does the separation efficiency of extractive distillation compare to that of azeotropic distillation?
Extractive distillation generally offers better separation efficiency than azeotropic distillation. This is because the solvent in extractive distillation forms a separate phase, whereas the entrainer in azeotropic distillation remains in the same phase as the mixture.
What is the role of temperature in extractive and azeotropic distillation?
Temperature plays a critical role in both extractive and azeotropic distillation as it affects the boiling point and vapor pressure of the components. In extractive distillation, the solvent’s boiling point should be higher than the components being separated, while in azeotropic distillation, the entrainer’s boiling point should be lower.
What is the most commonly used solvent in extractive distillation?
The most commonly used solvent in extractive distillation is water. Other solvents that are often used include glycols, alcohols, and ketones.
Can extractive distillation be used to separate components with large differences in boiling points?
Extractive distillation is not typically used to separate components with large differences in boiling points. In these cases, fractional distillation or other separation techniques may be more effective.
How does extractive distillation affect the purity of the separated components?
Extractive type distillation can produce high-purity separated components because the solvent selectively removes one component from the mixture. However, the solvent can also contaminate the separated component, so additional purification steps may be necessary.
What are the disadvantages of azeotropic distillation?
Azeotropic distillation has several disadvantages, including high energy consumption, the need for an entrainer, and the risk of forming new azeotropes. It can also be challenging to find a suitable entrainer for a particular mixture.
What are the advantages of azeotropic distillation?
Azeotropic distillation can separate components that have similar boiling points or form azeotropes, which is difficult to achieve with conventional distillation. It can also produce high-purity products and be used to recycle solvents.
How does the entrainer concentration affect the separation efficiency in azeotropic distillation?
The entrainer concentration can affect the separation efficiency in azeotropic distillation. If the entrainer concentration is too low, it may not alter the azeotrope’s composition sufficiently, whereas a high entrainer concentration can lead to excessive solvent usage and increased costs.
What are some common applications of azeotropic distillation?
Azeotropic distillation is commonly used in the production of specialty chemicals, such as solvents, polymers, and surfactants. It is also used in the production of biofuels and in the recycling of solvents.
Can extractive distillation be used for continuous separation?
Yes, extractive distillation can be used for continuous separation by continuously adding the solvent to the mixture and separating the two phases. This process can be performed using a packed column or tray column.
Conclusion
Distillation is a crucial separation technique used in various industries. Extractive and azeotropic distillation are two techniques used to separate components with similar boiling points or azeotropic mixtures. Extractive distillation involves the addition of a third component to facilitate separation, while azeotropic distillation involves boiling the components to form an azeotrope.
Read Also,