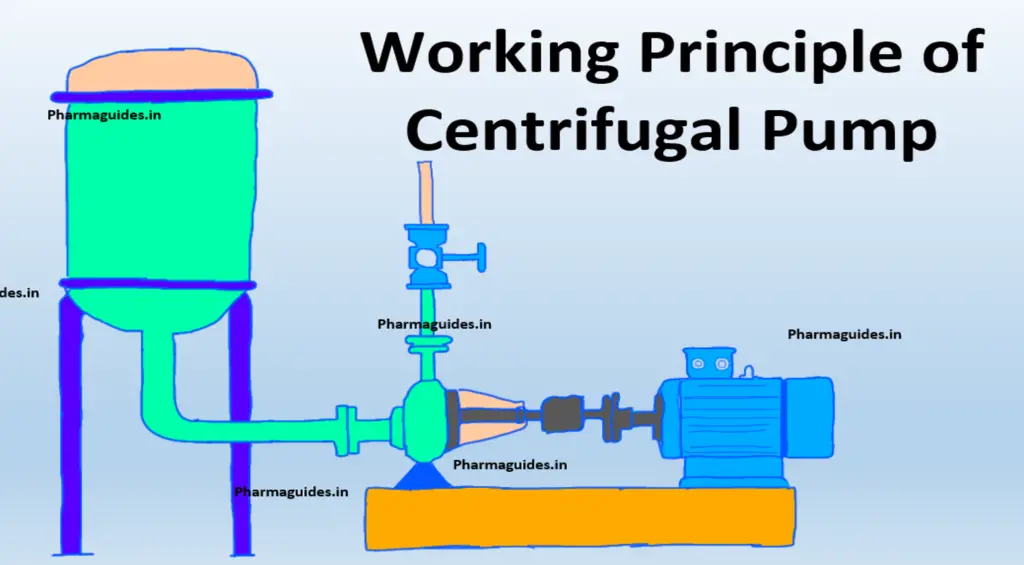
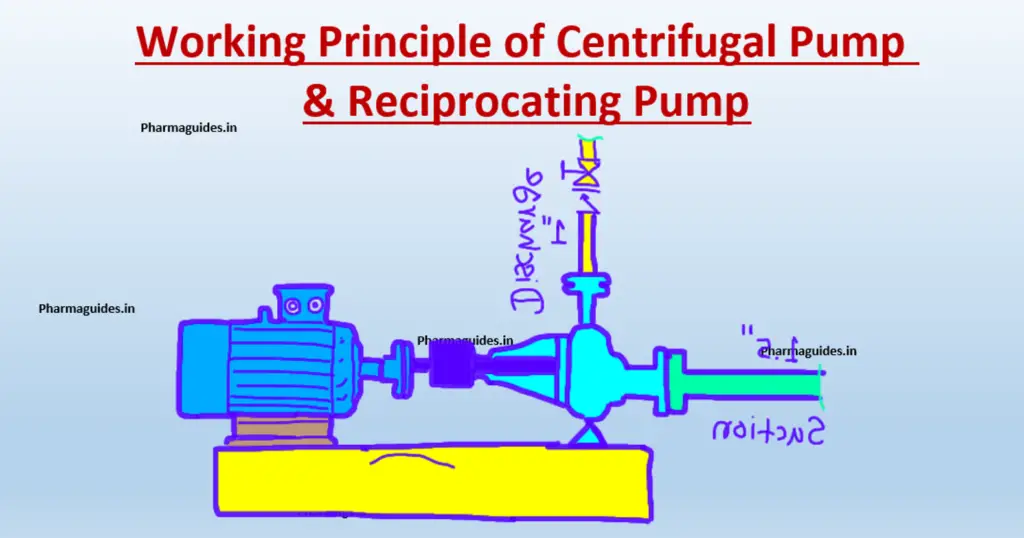
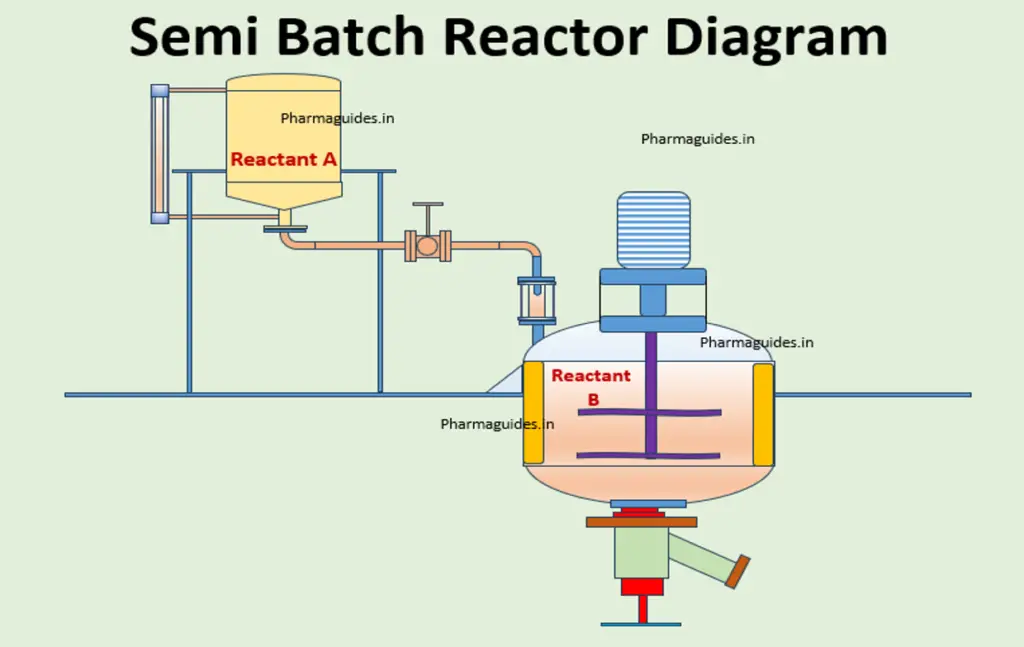
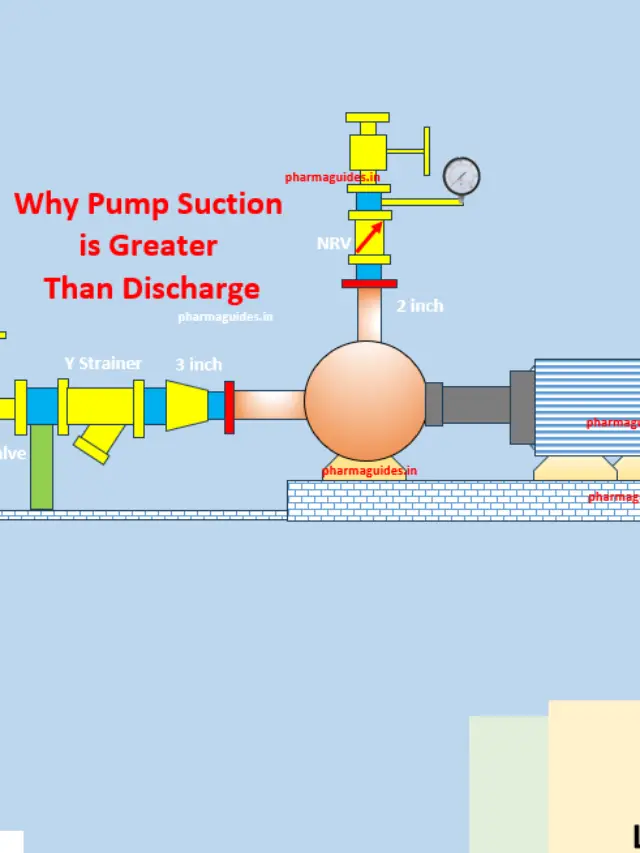
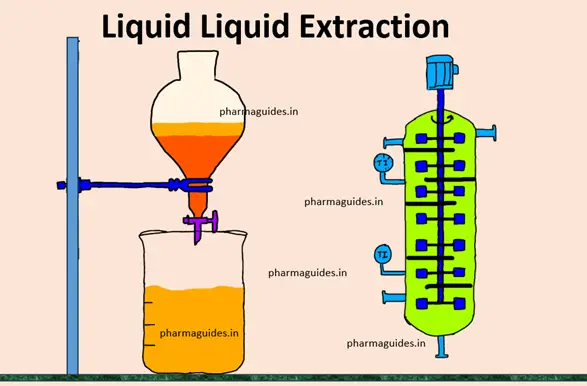
Programmable logic controller (PLC)
A programmable logic controller (PLC) is a specialized computer used to control machines and process.It uses a programmable memory to store instructions and specific functions that include On/Off control, timing, counting, sequencing, arithmetic, and data handling
Advantages of PLC Control
• Flexible
• Faster response time
• Less and simpler wiring
• Solid-state – no moving parts
• Modular design – easy to repair and expand
• Handles much more complicated systems
• Sophisticated instruction sets available
• Allows for diagnostics “easy to troubleshoot”
•
More Flexibility:
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) can provide system updates for a process by simply sending out a new program.
It is easier to create and change a program in a PLC than to wire and rewire a circuit. End-users can modify the program in the field.
Increased Reliability:
Once a program has been written and tested it can be downloaded to other PLCs.
Since all the logic is containedin the PLC’s memory, there is no chance of making a logic wiring error.
Lower Costs:
Originally PLCs were designed to replace relay control logic. The cost savings using PLCs have been so significant that relay control is becoming obsolete, except for power application
Generally, if an application requires more than about 6 control relays, it will usually be less expensive to install a PLC.

Communications Capability:
A PLC can communicate with other controllers or computer equipment.They can be networked to perform such functions as: supervisory control, data gathering, monitoring devices and process parameters, and downloading and uploading of programs
Faster Response Time:
PLCs operate in real-time which means that an event taking place in the field will result in an operation or output taking place.
Machines that process thousands of items per second and objects that spend only a fraction of a second in front of a sensor require the PLC’s quick response capability.
Modifying A PLC Program
If a relay system were used, it would require some rewiring of the system, as shown, to achieve the desired change.
PLC VRS PC
PLC
– Operates in the industrial environment
– Is programmed in relay ladder logic
– Has no keyboard, CD drive, monitor, or disk drive
– Has communications ports, and terminals for input and output devices
PC
– Some manufacturers have
software and interface cards available so that a PC can do the work of a PLC
– Some manufacturers have software and interface cards available so that a PC can do the work of a PLC
Typical PLC Instructions
XIC (Examine ON) . . . . Examine a bit for an ON condition
XIO (Examine OFF). .. . . Examine a bit for an OFF condition
OTE (Output Energize) . . . . Turn ON a bit (non retentive)
OTL (Output Latch) Latch a bit
OTU (Output Unlatch) . . . . Unlatch a bit
TOF (Timer Off-Delay) . . Turn an output ON or OFF afterits rung has been OFF a preset time interval
TON (Timer On-Delay) . . . . Turn an output ON or OFF after its rung has been ON for a preset time interval
CTD (Count Down) . . . . . . . Use a software counter to count down from a specified value
CTU (Count Up) . . . . . . . . . Use a software counter to count up
to a specified value
script async src="https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js">