short path distillation
Article Contents
Short Path Distillation
Distillation is a fundamental separation process used to purify liquids based on differences in their boiling points. It involves heating a liquid mixture to create vapor and then cooling that vapor to obtain a purified liquid. As the mixture is heated, components with lower boiling points vaporize first, and the vapor is condensed back into liquid form. This selective vaporization and condensation allow for the separation of components, producing a purified substance. Distillation is widely applied in industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and beverage production, playing a critical role in producing pure solvents, chemicals, and distilled beverages.

What is Short Path Distillation?
Short Path Distillation is an advanced technique that minimizes the distance between the evaporation surface and the condensation surface, reducing exposure to external elements. This precision ensures superior separation, especially for compounds with close boiling points.

Why Short Path Distillation?
Short Path Distillation is employed for various reasons, making it a preferred choice in specific scenarios where traditional distillation methods may fall short. Here are key reasons why Short Path Distillation is utilized:
- Thermal Sensitivity:
- Reason: Short Path Distillation is ideal for compounds sensitive to high temperatures. The reduced vapor travel distance minimizes thermal exposure, preventing thermal degradation of delicate substances.
- Precision Separation:
- Reason: The technique offers precise separation, particularly for mixtures containing components with very close boiling points. The minimized vapor path enhances separation efficiency, providing a distinct advantage over traditional distillation.
- High-Purity Products:
- Reason: Short Path Distillation is chosen when the goal is to achieve high-purity products. Its precision allows for the separation of compounds with minimal contamination, meeting the stringent purity requirements of industries like pharmaceuticals.
- Handling Complex Mixtures:
- Reason: It is applied when dealing with complex mixtures, such as those containing azeotropes or components with intricate compositions. Short Path Distillation overcomes challenges posed by traditional methods in handling these mixtures.
- Fragile or High-Value Compounds:
- Reason: Short Path Distillation is preferred for compounds that are fragile or of high value. The gentle distillation process minimizes the risk of thermal degradation, preserving the integrity of valuable or delicate substances.
- Research and Development:
- Reason: In research and development, where a deep understanding of the composition of mixtures is crucial, Short Path Distillation provides a tool for precise analysis and separation. It aids researchers in exploring new compounds and formulations.
- Reduced Environmental Impact:
- Reason: Short Path Distillation is chosen for its potential to reduce the environmental impact of distillation processes. Its energy-efficient design contributes to sustainability by minimizing energy consumption.
- Efficiency in Small-Scale Production:
- Reason: In small-scale production settings, where efficiency and product quality are paramount, Short Path Distillation offers a more controlled and efficient separation process compared to traditional methods.
- Selective Distillation:
- Reason: Short Path Distillation allows for selective distillation by minimizing the potential for undesired reactions. This is particularly advantageous when distilling compounds with reactive functional groups.
- Versatility in Industry:
- Reason: Its versatility makes Short Path Distillation suitable for various industries, including pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, and research, where precise separations are essential.
When Should Short Path Distillation Grace the Lab?
Short Path Distillation is a highly specialized technique, and its application is recommended in specific scenarios where traditional distillation methods may not be suitable. Here are situations when Short Path Distillation is particularly advantageous:
- Thermally Sensitive Compounds:
- Scenario: When working with compounds that are sensitive to high temperatures and prone to thermal degradation.
- Reason: Short Path Distillation minimizes the exposure of compounds to heat, making it ideal for handling thermally sensitive substances.
- Close Boiling Points:
- Scenario: When dealing with mixtures containing components with very close boiling points.
- Reason: The reduced vapor travel distance in Short Path Distillation enhances separation efficiency, allowing for the distillation of closely boiling substances.
- High-Purity Requirements:
- Scenario: When the goal is to achieve high-purity products with minimal contamination.
- Reason: Short Path Distillation provides precise separation, making it suitable for industries such as pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals with stringent purity requirements.
- Complex Mixtures:
- Scenario: When working with mixtures that present challenges in conventional distillation due to azeotropes or complex compositions.
- Reason: The precision of Short Path Distillation allows for effective separation in complex mixtures, overcoming challenges posed by traditional methods.
- Fragile or High-Value Compounds:
- Scenario: When handling compounds that are fragile or of high value.
- Reason: The gentle distillation process in Short Path Distillation minimizes the risk of thermal degradation, making it suitable for valuable or delicate substances.
- Research and Development:
- Scenario: During research and development phases where understanding the composition of mixtures is crucial.
- Reason: Short Path Distillation provides researchers with a tool for precise analysis and separation, aiding in the exploration of new compounds and formulations.
- Reduced Environmental Impact:
- Scenario: When environmental impact is a concern, and energy-efficient processes are desired.
- Reason: Short Path Distillation, by reducing the energy-intensive aspects of traditional distillation, contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly process.
- Small-Scale Production:
- Scenario: In small-scale production settings where efficiency and product quality are paramount.
- Reason: Short Path Distillation can be suitable for smaller batches, providing a more controlled and efficient separation process.
Process of Short Path Distillation
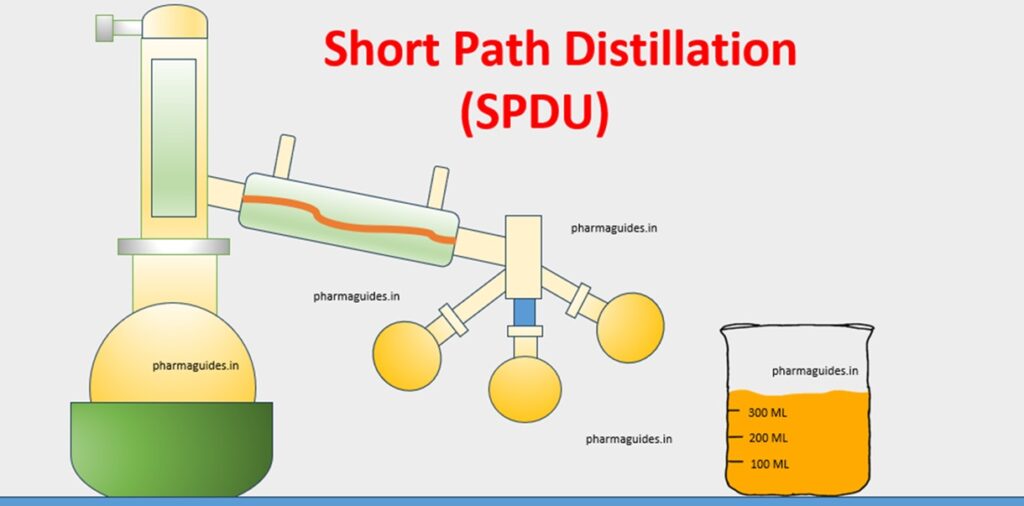
The process of Short Path kind of Distillation involves several steps, each contributing to the efficient separation of components with minimal thermal exposure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Setup of Apparatus:
- Arrange the Short Path kind of Distillation apparatus, including a heating mantle, distillation flask, short-path distillation head, condenser, and a collection flask.
- Loading the Mixture:
- Place the mixture requiring separation into the distillation flask. This mixture often contains substances with close boiling points or those sensitive to higher temperatures.
- Vacuum Setup:
- Initiate the vacuum system to reduce the pressure inside the system. Lowering the pressure lowers the boiling points of the compounds, aiding in the distillation process.
- Heating the Flask:
- Apply gentle heat to the heating mantle beneath the distillation flask. The heating process initiates the vaporization of components in the mixture.
- Vapor Travel:
- As vapors rise, they encounter the short-path distillation head. The reduced distance between the evaporation and condensation surfaces minimizes thermal exposure and accelerates the separation process.
- Condensation:
- Vapors travel through the short-path distillation head and reach the condenser. The condenser cools the vapors, causing them to condense back into liquid form.
- Collection:
- The condensed liquid, now enriched with separated components, collects in the receiving flask. Each compound is collected in distinct fractions based on its boiling point.
- Monitoring and Adjustment:
- Throughout the process, monitor the temperature, pressure, and collection rate. Adjust parameters as needed to optimize separation efficiency.
- Analysis of Fractions:
- Analyze the collected fractions for purity and composition. This step ensures the success of the separation process and provides valuable data for process optimization.
- Cleanup and Maintenance:
- Once the distillation is complete, shut down the apparatus, clean the components, and perform any necessary maintenance to prepare for future distillation runs.
Unit of Short Path Distillation
The apparatus typically comprises a heating mantle, a distillation flask, a condenser, and a collection flask. The compact design ensures efficient vapor travel, minimizing the chance of undesired reactions.
Short Path Distillation Principle
The principle of Short Path kind of Distillation lies in minimizing the distance traveled by vapors during the distillation process. By reducing the path between the evaporation surface and the condensation surface, this technique mitigates the exposure of compounds to external elements, minimizing thermal decomposition. The shortened path allows for distillation at lower temperatures, preserving the integrity of thermally sensitive compounds. This precision in vapor travel enhances separation efficiency, making Short Path Distillation an ideal choice for achieving precise separations, especially for substances with close boiling points or those prone to thermal degradation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Short Path Distillation
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Separation Efficiency | – Enhanced separation efficiency due to reduced vapor travel distance. | – Equipment complexity may require skilled operators. |
| Thermal Exposure | – Reduced thermal exposure to compounds, making it ideal for thermally sensitive substances. | – Higher initial investment compared to traditional distillation methods. |
| Suitability for Sensitive Compounds | – Ideal for distilling thermally sensitive compounds at lower temperatures. | – May not be necessary for simple, non-sensitive separations where traditional methods suffice. |
| Precision in Distillation | – Precision in separation, minimizing the risk of undesired reactions and compound degradation. | |
| Equipment Design | – Compact design with a heating mantle, distillation flask, condenser, and collection flask for efficient vapor travel. | |
| Ease of Operation | – Efficient vapor travel minimizes the chance of undesired reactions, providing ease of operation. | |
| Applications | – Widely used in industries requiring high purity, such as pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals. |
This table provides a concise overview of the advantages and disadvantages associated with Short Path Distillation, offering insights into its suitability for various applications and potential challenges in its implementation.
Q&A on Short Path Distillation: Navigating Complexity
Q: What makes short path distillation superior?
A: Its precision and reduced thermal exposure make it superior for separating delicate compounds.
Q: When is short path distillation not recommended?
A: It may not be necessary for simple, non-sensitive separations where traditional methods suffice.
What is Short Path Distillation?
Short Path Distillation is an advanced separation technique that minimizes the distance between the evaporation and condensation surfaces during the distillation process. This precision reduces thermal exposure and is particularly beneficial for compounds with close boiling points or those sensitive to high temperatures. Short Path Distillation enhances separation efficiency, making it a preferred method for achieving high-purity products in industries such as pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals.
What is Simple Distillation in Short?
Simple distillation is a basic separation process where a liquid mixture is heated, and the vapor is condensed to obtain purified components. It is suitable for substances with significantly different boiling points. While it provides a straightforward separation, it may not be as effective for mixtures with closely boiling components.
What is the Process of Distillation in Short?
The distillation process involves heating a liquid mixture to create vapor and then cooling that vapor to obtain purified liquid components. As the mixture is heated, components with lower boiling points vaporize first, and the condensed vapor results in the separation of components based on their boiling points. Distillation is widely used across industries for purifying liquids, producing high-purity solvents, chemicals, and distilled beverages.
What is Distillation in Very Short?
Distillation is a separation process where a liquid mixture is heated to create vapor, and the vapor is then condensed to obtain purified liquid components. It exploits differences in boiling points to separate substances. Distillation is widely applied in industries to produce pure solvents, chemicals, and beverages, playing a crucial role in achieving high-purity end products.
Conclusion
In the intricate world of distillation, Short Path Distillation emerges as a beacon of precision. Its ability to delicately handle thermally sensitive compounds and provide unparalleled purity makes it an indispensable tool in the pursuit of excellence in chemical separation. As technology advances, Short Path Distillation continues to carve a path toward unprecedented precision in the laboratory.
What is Destructive Distillation
short path distillation principle
disadvantages of short path distillation
Fractional Distillation of Petroleum
Explain the Process of Fractional Distillation of Petroleum
Fractional Distillation of Petroleum Diagram